Global Electricity Review 2024: Goals, Contradictions, and Investments
Introduction
The Global Electricity Review 2024 provides a comprehensive overview of recent developments in global electricity generation, focusing on the expansion of renewable energy, the continued reliance on fossil fuels, and investment trends worldwide. The report emphasizes the rapid growth of renewable energy capacity, particularly solar and wind, while highlighting significant challenges that hinder a full transition to clean energy. This analysis delves into the report’s main goals, contradictions, and investments, supported by numerical data, offering insights into the global energy landscape.
The report paints a complex picture of both progress and setbacks, revealing the intricate dynamics of the global energy transition and the efforts needed to overcome the remaining barriers. It provides a roadmap for how renewable energy can take center stage in the fight against climate change while also emphasizing the urgency of addressing the persistent reliance on fossil fuels. The findings underscore the importance of collaboration, innovation, and strategic investments in achieving a sustainable energy future.
Goals
The primary goals outlined in the Global Electricity Review 2024 center on increasing the share of renewable energy in global electricity production, reducing carbon emissions, and accelerating the transition to clean energy while improving energy efficiency. These goals are framed within the broader context of meeting global climate targets, particularly those set out in the Paris Agreement, which seeks to limit global temperature rise to 1.5°C. Achieving these goals requires coordinated international efforts, substantial investments, and strategic policy frameworks that incentivize renewable energy adoption across diverse regions.
Increasing the Share of Renewable Energy
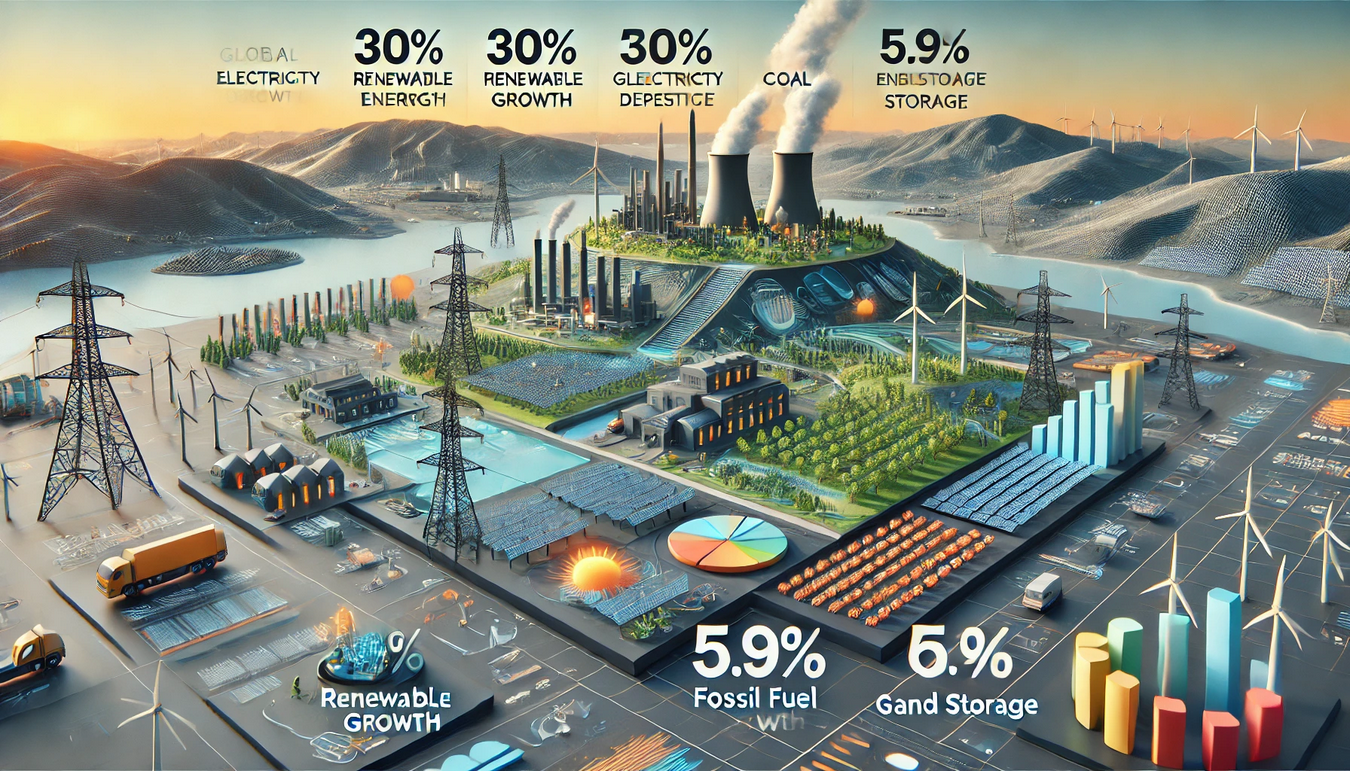
One of the foremost goals is to increase the share of renewable energy, particularly solar and wind, in global electricity production. As of 2023, renewables accounted for 30% of global electricity generation—a record high. The ambition is to push this growth further, with a target of solar and wind replacing coal and natural gas as the dominant sources of electricity by 2030. Achieving this goal necessitates not only technological advancements but also a supportive policy environment that encourages investment in renewable infrastructure and reduces barriers to entry.
Specific Goals:
- Triple Renewable Energy Capacity by 2030: The report sets an ambitious target to achieve a threefold increase in solar and wind capacity within the next seven years, enabling renewables to meet 60% of global electricity demand by the decade’s end. This will require unprecedented levels of international cooperation, technological innovation, and policy alignment, focusing on both developed and developing nations to ensure an equitable energy transition.
Reducing Carbon Emissions and Meeting Climate Targets
Another critical goal is to peak carbon emissions from electricity generation by 2023, followed by substantial reductions. This goal is pivotal for aligning global electricity generation with climate targets set by the Paris Agreement. The report emphasizes that reducing carbon emissions from the power sector is essential, given that it remains one of the largest contributors to global greenhouse gas emissions.
Specific Goals:
- Reduce Coal and Natural Gas Usage: The aim is to phase out coal, particularly in regions where it remains the dominant energy source, such as Asia, and to reduce reliance on natural gas as renewable energy capacity expands. Achieving this will require a combination of policy measures, including carbon pricing, subsidies for clean energy, and investments in cleaner technologies.
Accelerating the Transition to Clean Energy and Improving Energy Efficiency
To meet the growing demand for electricity driven by the electrification of transport, industry, and residential sectors, the report calls for a doubling of energy efficiency by 2030. Improving energy efficiency is crucial not only for reducing overall energy consumption but also for maximizing the benefits of renewable energy by ensuring that electricity is used as effectively as possible. The report also highlights the importance of advancements in grid infrastructure and energy storage technologies, which are essential for integrating variable renewable sources like wind and solar into the power system.
Specific Goals:
- Increase Energy Storage and Grid Integration: To compensate for the variability of renewable energy sources, significant advancements in energy storage and grid integration are needed. Energy storage technologies, such as batteries, will play a key role in stabilizing the supply of electricity, while improvements in grid infrastructure will help manage electricity distribution more effectively, thereby reducing waste and ensuring reliability.
Expanding Clean Electricity Infrastructure
The report underscores the importance of expanding clean electricity infrastructure to meet growing energy demands. This will involve substantial investments in new generation capacity, grid modernization, and the development of smart grids that can dynamically respond to changes in electricity demand and supply. Additionally, expanding infrastructure must include microgrids in remote areas to ensure that all communities have access to clean, reliable energy.
Contradictions
The Global Electricity Review 2024 also identifies several contradictions that hinder the full realization of its clean energy goals. These contradictions arise primarily from the continued dependence on fossil fuels, regional disparities in renewable energy investment, and challenges related to the mismatch between capacity additions and actual generation output.
Dependence on Fossil Fuels Despite Renewable Growth
Despite the strong growth in renewable energy, fossil fuel use, particularly coal, increased in several regions in 2023. This was particularly evident in countries like China and India, where hydropower generation was reduced due to drought conditions, leading to an increased reliance on coal to meet electricity demand. This dependence on fossil fuels highlights the challenges of transitioning to a fully renewable energy system, especially in regions where renewable infrastructure is still developing.
Numerical Contradiction:
- In 2023, global coal consumption grew by 5.9%, contributing to higher emissions. This growth underscores the need for more resilient renewable energy systems that can withstand climatic variability and reduce dependence on fossil fuels during periods of disruption.
- Coal usage in 2023 added an additional 307 MtCO2 of emissions, directly contradicting the goal of reducing carbon dioxide emissions.
Regional Disparities in Investment and Renewable Energy Adoption
The report highlights significant regional disparities in renewable energy investment and adoption. Countries such as China and the Netherlands have made considerable progress, while regions like Africa and South Asia lag behind due to a lack of financial resources and infrastructure. These disparities are a major obstacle to achieving global climate targets, as they prevent many countries from transitioning away from fossil fuels.
Numerical Contradiction:
- Africa, which accounts for one-fifth of the global population, received only 3% of global energy investments in 2023, despite its vast potential for solar energy. Bridging this investment gap will require targeted international support and the establishment of financing mechanisms that lower the cost of capital for renewable projects in underfunded regions.
- China accounted for over 50% of global wind and solar additions in 2023, highlighting the significant imbalance in renewable energy investment. Concentrating renewable investments in a few regions leaves other parts of the world vulnerable to continued reliance on fossil fuels, hampering global decarbonization efforts.
Mismatch Between Capacity Additions and Generation Output
While solar and wind capacity expanded significantly in 2023, actual electricity generation from these sources fell short of expectations due to delayed installations and lower sunlight levels. This mismatch reveals the complexities involved in deploying renewable energy technologies at scale and underscores the need for better planning, timely execution of projects, and technologies that mitigate the effects of unfavorable weather conditions.
Numerical Contradiction:
- Solar generation increased by only 23%, falling short of the expected 29%, due to reduced solar insolation and late installations. This shortfall highlights the importance of improving project timelines and adopting technologies that optimize energy capture.
- A generation shortfall of 51 TWh was attributed to less sunny weather and underreporting, emphasizing the need for accurate forecasting and reporting.
Continued Use of Fossil Fuels
Despite significant growth in renewable energy capacity, fossil fuel use rose by 5.9% globally in 2023. This increase was largely driven by countries like China, where electricity demand outpaced the availability of renewable energy, partly due to poor hydropower conditions. The continued reliance on fossil fuels, even as renewable capacity expands, indicates that the transition to clean energy is not happening quickly enough to meet global climate targets.
Numerical Contradiction:
- China’s coal generation increased by 5.9% in 2023, leading to a corresponding rise in emissions, even though the country added more than half of the world’s new solar and wind generation. This paradox highlights the difficulty of balancing growing energy demand with the need to reduce emissions, especially in rapidly developing economies.
Underreporting and Grid Congestion
Countries with substantial renewable capacity additions, such as China and Japan, faced challenges related to underreporting of actual generation and grid congestion. Underreporting skews data and leads to incorrect assessments of progress, while grid congestion prevents electricity from being delivered effectively to consumers, thus hindering the full utilization of renewable energy capacity.
Numerical Contradiction:
- In countries like Japan and California, grid congestion and curtailment prevented renewable energy from being fully utilized, despite significant capacity additions. Investments in grid expansion and modernization are necessary to alleviate these bottlenecks and improve electricity distribution efficiency.
Investments
The Global Electricity Review 2024 emphasizes the critical role of investments in renewable energy, grid infrastructure, and energy storage in driving the global energy transition. However, the report also highlights significant disparities in investment, both across regions and in terms of the types of projects receiving funding.
China’s Renewable Energy Investments and Continued Fossil Fuel Use
China led the world in renewable energy investments, contributing over 50% of global wind and solar additions in 2023. However, the simultaneous expansion of coal capacity complicates the transition away from fossil fuels. The dual approach of expanding both renewable and fossil fuel capacities reflects the complexities faced by rapidly growing economies that must balance energy security with climate commitments.
Investment Figures:
- China accounted for 60% of global solar energy growth and 50% of wind energy growth in 2023, yet coal generation increased by 5.9%. This duality indicates that while progress is being made in renewable energy, parallel efforts are needed to reduce dependence on coal and other fossil fuels to align with climate goals.
Regional Disparities in Investment
There are stark regional differences in clean energy investments, with China and the European Union leading the way, while Africa and parts of South Asia continue to struggle with limited resources and high financing costs. These disparities hinder the global transition to clean energy by preventing many regions from taking full advantage of renewable technologies.
Investment Figures:
- Africa received only 3% of global energy investments in 2023, despite its significant potential for solar energy. Addressing this investment gap will require innovative financing solutions, including public-private partnerships and international climate funds aimed at supporting renewable projects in underdeveloped regions.
Lagging Grid Infrastructure Investments
The report stresses the need for increased investments in grid infrastructure and energy storage technologies to fully harness the potential of growing renewable energy capacity. Without such investments, grid congestion and curtailment limit the benefits of added renewable capacity, ultimately hindering progress toward clean energy goals.
Investment Figures:
- Investments in grid infrastructure are crucial to reducing curtailment, particularly in regions like China and California. Ensuring that renewable energy can be efficiently transmitted from production sites to areas of demand will maximize the value of these investments and help stabilize electricity supplies.
Conclusion
The Global Electricity Review 2024 highlights significant progress in the growth of renewable energy, yet reveals critical contradictions that hinder the full realization of clean energy goals. Despite substantial investments in solar and wind energy, fossil fuel use continues to rise in several regions, and infrastructure limitations prevent renewable capacity from being fully utilized. The mismatch between renewable capacity additions and actual generation output, along with regional disparities in investment, underscores the need for further investments in grid modernization, energy storage, and international collaboration.
Addressing these challenges will require sustained political will, innovative financing, and a focus on equity to ensure that all regions can transition to clean energy. The global energy transition remains complex, but with continued efforts, it is possible to align investments and policies with long-term climate goals. Achieving this alignment will depend on addressing the structural issues that currently limit renewable adoption, such as inadequate infrastructure, financial barriers, and regional disparities in access to technology. With a concerted effort, the vision of a sustainable, low-carbon energy future can be realized, ultimately helping to mitigate climate change and improve energy security worldwide.